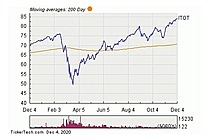
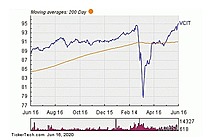
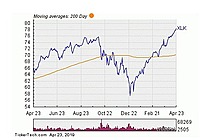
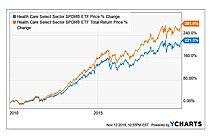
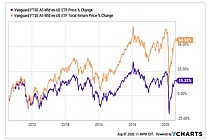
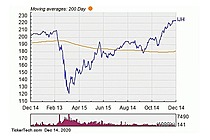
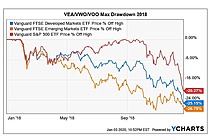
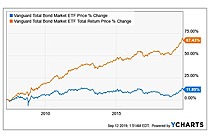
Exchange Traded Fund
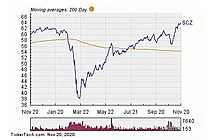
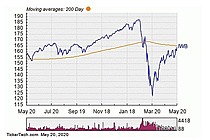
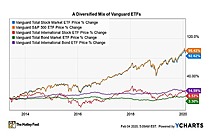
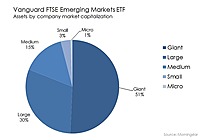
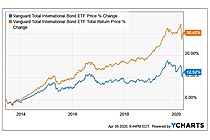
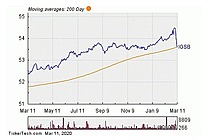
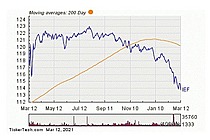
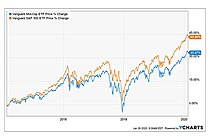
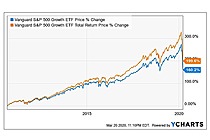
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is a form of securities that trade on an exchange that contains many types of investments, including stocks, commodities, bonds, or a mixture of investment types. Considered as a marketable security, ETFs are easily bought and sold, offering the best attributes with lower fees and tax-efficiency. A one-size-fits-all solution, ETFs combine the features of a mutual fund, with the intraday trading feature of a closed-end fund. ETFs can be more cost-effective and more liquid than mutual funds, enabling them to have more diversification benefits while also mimicking the ease with which stocks are traded.
Experts
Jeremy Deems
Adam Butler
Albert Yeh
Andy Clarke
Aniket Ullal
Ari Pine
Ari Wald
Art Hogan
Arthur Hayes
Bill Lipschutz
Bill Strazzullo
Blair Hull
Bob Froehlich
Bob Iaccino
Brendan Ahern
Brett Harrison
Brian Portnoy
Brian Taylor
Bud King
Charles Biderman
Charles Noble III
Chris Berry
Chris Hausman
Christian Fromhertz
Christine Sandler
Corey Hoffstein
Dan Ahrens
Dan Bortolotti
Daren Riley
Dave Mazza
David Berns
David Kotok
David Stevenson
David Trainer
Doug Eberhardt
Ed Campbell
Edwin Choi
Edwin Elton
Eli Rauch
Eric Weigel
Erik Conley
Euan Sinclair
Francis Gannon
Frank Holmes
Frank Serebrin
Geoffrey Webster
George Douglas
George Milling-Stanley
George Patterson
Greg King
Harry Clark
Imran Lakha
Irina Dorogan
James Davolos
James Seyffart
Jamie Coutts
Jan van Eck
Janet Brown
Jared Dillian
Jason Bodner
Jason Katz
Jason Kelly
Jason Richey
Jay Jacobs
Jay Pelosky
Jeff Kilburg
Jeff Marcus
Jeff Ross
Jeffrey Hirsch
Jeremy Schwartz
Jerry Hwang
Jessica Rabe
Jim Masturzo
Jim O'Shaughnessy
Joe Cavatoni
John Bartlett
John Ciampaglia
John Murphy
John Netto
Jonathan DeYoe
Jonathan Krane
Jono Steinberg
Kathleen Moriarty
Kathy Lien
Katrina Radenberg
Keith Dicker
Kevin O'Leary
Kristen Capuano
Larry Raffone
Lee Robertson
Leland Clemons
Liqian Ren
Lucas Downey
Lyn Alden
Marc Chaikin
Marc Mayer
Marc Pfeffer
Marie Dzanis
Mark Newton
Martin Gruber
Matt Hougan
Matt McCall
Matt Tucker
Matthew Tuttle
Matthew Waz
Micah Wakefield
Michael Corcelli
Michael Gayed
Michael Pento
Michael Steinhardt
Michael Venuto
Mick McLaughlin
Mike Philbrick
Morgan Paxhia
Moss Crosby
Nigam Arora
Noah Hamman
Noreen Beaman
Patrick Ceresna
Patrick Watson
Paul Kim
Paul Krake
Peter Churchouse
Rayne Steinberg
Rick Pendergraft
Roji Abraham
Ron Rowland
Ron Vinder
Royce Running
Russ Koesterich
Russell Wild
Saker Nusseibeh
Sam Bankman-Fried
Scott Dooley
Shundrawn Thomas
Stephanie Pierce
Stephen Burke
Steve Blumenthal
Steve Craig
Steve Ehrlich
Steve Hawkins
Steven Schoenfeld
Tariq Dennison
Thejas Nalval
Tim Maloney
Tim Price
Tom Jacobs
Tommy Thornton
Tony Crescenzi
Tony Sagami
Tony Zhang
Will Hershey
Will Rhind
Xavier Rolet